Understanding the Steel Fabrication Shop Process
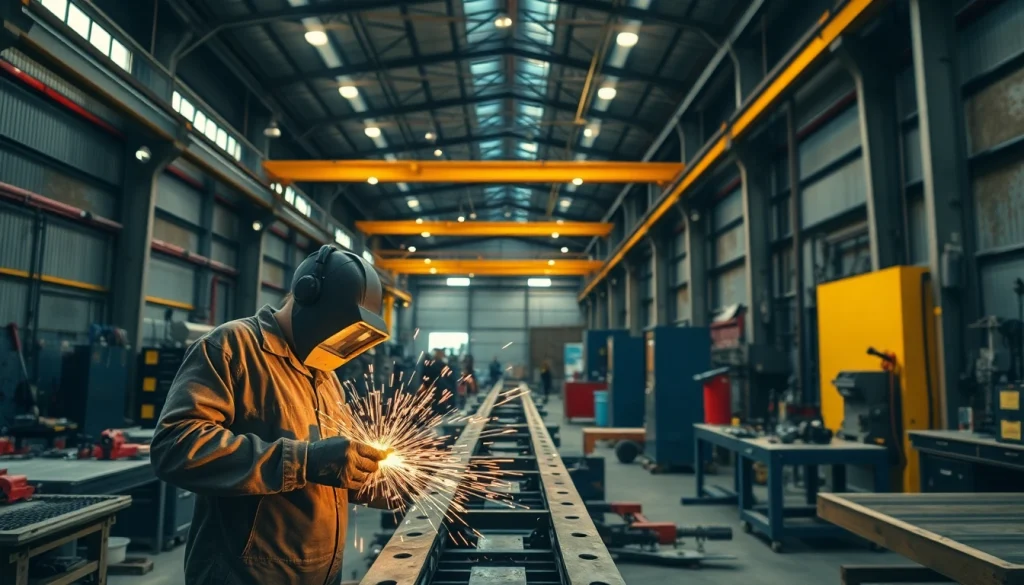
The steel fabrication shop serves as the backbone for numerous sectors, including construction, manufacturing, and engineering. A thorough understanding of its processes is essential for anyone involved in these industries. Within a steel fabrication shop, raw steel materials undergo various processes that transform them into structures and components vital for modern infrastructure. This article takes an in-depth look at these processes, tools, safety practices, quality assurance, innovations, and efficiency strategies critical to a successful steel fabrication operation.
Overview of Steel Fabrication Techniques
Steel fabrication involves several techniques that hinge on the project requirements, material types, and desired outcomes. The primary methods include:
- Cutting: Various methods such as sawing, shearing, and plasma cutting are employed to shape steel materials to precise dimensions.
- Bending: Utilizing press brakes or rolling machines, steel components can be bent to required angles or shapes.
- Welding: This technique joins metal parts together using heat and filler materials, resulting in robust structures.
- Machining: Involves removing material to achieve desired specifications and fine tolerances, often using lathes, mills, and drills.
- Assembling: This final stage entails combining fabricated components into a completed structure, often bolted or welded together.
Mastering these techniques is crucial for enhancing the durability and integrity of the final products.
Key Equipment and Tools Used in Steel Fabrication Shop
An effective steel fabrication shop relies on a variety of specialized tools and equipment. Key examples include:
- Plasma Cutters: Used for cutting metal sheet and fabricated components with precision.
- Welding Machines: Essential for various types of welding including MIG, TIG, and arc welding.
- Press Brakes: Used to bend sheet metal into specific angles and shapes with extreme accuracy.
- Band Saws: Perfect for cutting steel and other materials efficiently.
- CNC Machines: Equipped for computer-controlled cutting and machining, improving precision and reducing waste.
Each piece of equipment plays a vital role in expediting fabrication tasks while ensuring high-quality outcomes.
Common Materials in Steel Fabrication
A variety of materials are used in steel fabrication, each providing unique properties suitable for specific applications:
- Carbon Steel: Known for its strength and versatility, carbon steel is a popular choice in construction.
- Stainless Steel: Recognized for its corrosion resistance, it is frequently used in food processing and medical applications.
- Alloy Steel: Incorporates other elements to enhance specific characteristics such as strength and toughness.
- Tool Steel: Designed for manufacturing tools and dies, offering exceptional hardness and resistance to abrasion.
Understanding the properties of these materials enables better selection based on project needs, ensuring successful outcomes.
Safety Best Practices in the Steel Fabrication Shop
Safety remains a paramount concern within the steel fabrication shop. Implementing robust safety practices protects employees and optimizes operations.
Personal Protective Equipment Essentials
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is vital for safeguarding workers in a fabrication environment. Essential gear includes:
- Safety Glasses: Protect the eyes from debris and hazardous materials.
- Hard Hats: Prevent head injuries from falling objects.
- Steel-Toed Boots: Offer support and protection for feet in case of heavy machinery accidents.
- Gloves: Essential for preventing cuts and abrasions when handling steel materials.
- Respirators: Important in protecting against inhalation of harmful dust and fumes.
Ensuring all personnel are equipped with appropriate PPE not only enhances safety but also cultivates a culture of care and responsibility within the shop.
Hazard Recognition and Training
Regular training on hazard recognition is key to preventing workplace injuries. This should cover:
- Identifying Hazards: Training workers to recognize potential hazards such as moving equipment, hot surfaces, and chemical exposure.
- Safety Protocols: Establishing clear protocols for operating equipment safely and efficiently.
- Incident Reporting: Encouraging prompt reporting of safety incidents and near misses can help in identifying recurring issues.
Creating a safety-conscious workforce significantly mitigates risks and enhances overall operational performance.
Emergency Response Procedures
No workplace is immune to accidents; hence, having a robust emergency response procedure is essential. Key components include:
- Evacuation Plans: Clear signage and mapped-out evacuation routes ensure safety during emergencies.
- First Aid Kits: Accessible and well-stocked first aid kits should be available, along with trained personnel.
- Regular Drills: Conducting regular emergency drills familiarizes employees with procedures and reduces panic in real emergencies.
By implementing these procedures, the fabrication shop can significantly lessen the impact of any emergencies that occur.
Quality Control Measures in Steel Fabrication
Consistently delivering high-quality products is essential for retaining client trust and driving business growth. Quality control measures are integral to achieving superior results.
Importance of Inspections and Testing
Regular inspections and testing of fabricated materials and components can reveal defects before they progress into larger problems. This includes:
- Visual Inspections: Routine checks for surface flaws, misalignment, or other visible issues.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Employing methods like ultrasonic and radiographic testing to detect internal flaws without damaging components.
Implementing robust inspection routines can lead to enhanced safety and product reliability.
Using Technology for Quality Assurance
Technology plays an increasingly vital role in quality assurance within the steel fabrication shop:
- Automated Quality Inspections: Cameras and sensors equipped with machine learning can identify defects faster and more accurately than human inspections.
- Software Solutions: Quality management systems (QMS) enable tracking of all processes, documentation, and inspections, streamlining compliance and improving traceability.
Utilizing advanced technology not only boosts quality but also enhances operational efficiencies.
Implementing Standards and Certifications
Committing to industry standards and acquiring certifications guide processes towards higher quality benchmarks. Common standards include:
- ISO 9001: Ensures the establishment of a quality management system.
- ASME Certification: Recognizes adherence to specific engineering and manufacturing practices.
These certifications assure clients of consistent quality and reliability in products.
Innovative Trends in Steel Fabrication Shop
Innovation is at the heart of progress in the steel fabrication industry, continually reshaping how shops operate.
Automation and Robotics in Fabrication
Robotics and automation technologies are streamlining operations within steel fabrication shops, leading to:
- Increased Efficiency: Automated machines can operate at speeds unattainable by manual labor, limiting downtime.
- Enhanced Precision: Robotics allow for highly accurate cuts and welds, reducing material waste.
Integration of these technologies is transforming the traditional landscape of fabrication.
Eco-Friendly Practices in Steel Fabrication
As sustainability becomes a global imperative, steel fabrication shops are adopting eco-friendly practices:
- Waste Minimization: Implementing lean manufacturing techniques helps in reducing material waste at all stages of production.
- Recycling and Reusing Materials: Using recycled steel can significantly decrease environmental footprints.
Transitioning towards sustainability not only mitigates environmental impact but may also lead to cost savings and increased market competitiveness.
3D Printing and Its Impact on the Industry
3D printing technology is emerging as a complement to traditional steel fabrication, providing unique benefits such as:
- Rapid Prototyping: Accelerating the design process by quickly producing prototypes for testing and validation.
- Complex Geometries: Allowing the creation of intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
The integration of 3D printing could redefine traditional fabrication, making it more agile and responsive to client needs.
Improving Efficiency in Your Steel Fabrication Shop
Maximizing efficiency in a steel fabrication shop translates directly to better output, reduced overhead, and greater profitability.
Streamlining Workflow and Operations
Achieving a streamlined workflow is crucial for operational success. Strategies include:
- Layout Optimization: Arranging tools and workstations to minimize movement and reduce time wasted.
- Lean Manufacturing Principles: Adopting practices that prioritize efficiency, reduce waste, and improve output quality.
Effective workflow management dramatically enhances productivity levels.
Employee Training and Development Programs
Investing in staff development ensures that workers are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge. This can be executed through:
- Regular Workshops: Conducting workshops on new techniques, tools, and safety protocols helps staff stay current.
- Mentorship Programs: Pairing less experienced employees with seasoned veterans cultivates a strong foundation in essential skills.
Continuous training not only improves worker competency but also boosts morale and job satisfaction.
Performance Metrics to Track Shop Success
Tracking performance metrics is vital for assessing operational success. Key indicators to monitor include:
- Production Rates: Measuring the output against planned production goals.
- Quality Rates: Analyzing the percentage of products that meet quality standards versus those that do not.
- Safety Incident Rates: Keeping tabs on the frequency of incidents to assess the effectiveness of safety protocols.
By regularly monitoring these metrics, fabrication shops can identify areas for improvement, optimizing overall performance.